This guide describes how to run StarlingX in a set of VirtualBox VMs, which is an alternative to the default StarlingXinstructions using libvirt.
The guest has a virtual serial port that is passed through to the host's physical serial port /dev/ttyS0. In the guest, a legacy application communicates through this virtual serial port. In particular, it retrieves data from an external device; this data transfer usually lasts about 1 minute. Configure your VirtualBox virtual machine to have a serial port. For that, use the following settings in the configuration dialog for your VM: serial port: enable; port number: COM1; IRQ and port settings: ignore, use the defaults; Port Mode: Host Device; Port Path: /dev/ttyS0; Start the Windows XP guest OS and add the COM port to Windows XP.
A Windows or Linux computer for running VirtualBox.
VirtualBox is installed on your computer. The latest verified version is5.2.22. Download from: http://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
VirtualBox Extension Pack is installed.To boot worker nodes via the controller, you must install theVirtualBox Extension Pack to add support for PXE boot of Intel cards. Downloadthe extension pack from: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
Note
A set of scripts for deploying VirtualBox VMs can be found in theSTX tools repository,however, the scripts may not be updated to the latest StarlingXrecommendations.
For each StarlingX host, configure a VirtualBox VM with the following settings.
Note
The different settings for controller, worker, and storage nodes areembedded in the particular sections below.
OS type and memory settings¶
Football manager download free. Type: Linux
Version: Other Linux (64-bit)
Memory size:
Controller node: 16384 MB
Worker node: 8192MB
Storage node: 4096 MB
All-in-one node: 20480 MB
Disk(s) settings¶
Softing opc ua client. Use the default disk controller and default disk format (for example IDE/vdi)for VirtualBox VMs.
Minimum disk size requirements:
Controller nodes (minimum of 2 disks required):
Disk 1: 240GB disk
Disk 2: 10GB disk (Note: Use 30GB if you are planning to work on theanalytics.)
Worker nodes: 80GB root disk (Note: Use 100GB if you are installingStarlingX AIO node.)
When the node is configured for local storage, this will provide ~12GB oflocal storage space for disk allocation to VM instances.
Additional disks can be added to the node to extend the local storagebut are not required.
Storage nodes (minimum of 2 disks required):
80GB disk for rootfs.
10GB disk (or larger) for each OSD. The size depends on how many VMs youplan to run.
Storage tree, see empty CD-ROM. Click cd-rom, click
+to choose a CD/DVDiso, and browse to ISO location. Use this ISO only for the first controllernode. The second controller node and worker nodes will network boot from thefirst controller node.
System settings¶
System->Motherboard:
Boot Order: Enable the Network option. Order should be: Floppy, CD/DVD,Hard Disk, Network.
System->Processors:
Contract vanzare cumparare auto germania pdf download online. Controller node: 4 CPU
Worker node: 3 CPU
Note
This will allow only a single instance to be launched. More processorsare required to launch more instances. If more than 4 CPUs areallocated, you must limit vswitch to a single CPU before unlocking yourworker node, otherwise your worker node will reboot in a loop(vswitch will fail to start, in-test will detect that a critical servicefailed to start and reboot the node). Use the following command to limitvswitch:
Storage node: 1 CPU
Network settings¶
The OAM network has the following options:

Host Only Network - Strongly Recommended. This optionrequires the router VM to forward packets from the controllers to the externalnetwork. Follow the instructions at Install VM as a routerto set it up. Create one network adapter for external OAM. The IP addressesin the example below match the default configuration.
VirtualBox: File -> Preferences -> Network -> Host-only Networks. Click
+to add Ethernet Adapter.Windows: This creates a
VirtualBoxHost-onlyAdapterand promptswith the Admin dialog box. ClickAcceptto create an interface.Linux: This creates a
vboxnet<x>per interface.
External OAM: IPv4 Address: 10.10.10.254, IPv4 Network Mask: 255.255.255.0,DHCP Server: unchecked.
NAT Network - This option provides external network access to the controllerVMs. Follow the instructions at Add NAT Network in VirtualBox.
Adapter settings for the different node types are as follows:
Controller nodes:
Adapter 1 setting depends on your choice for the OAM network above. It canbe either of the following:
Adapter 1: Host-Only Adapter; VirtualBox Host-Only Ethernet Adapter 1),Advanced: Intel PRO/1000MT Desktop, Promiscuous Mode: Deny
Adapter 1: NAT Network; Name: NatNetwork
Adapter 2: Internal Network, Name: intnet-management; Intel PRO/1000MTDesktop, Advanced: Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Worker nodes:
Adapter 1:
Internal Network, Name: intnet-unused; Advanced: IntelPRO/1000MT Desktop, Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Adapter 2: Internal Network, Name: intnet-management; Advanced: IntelPRO/1000MT Desktop, Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Adapter 3: Internal Network, Name: intnet-data1; Advanced:Paravirtualized Network (virtio-net), Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Windows: If you have a separate Ubuntu VM for Linux work, then addanother interface to your Ubuntu VM and add it to the sameintnet-data1 internal network.
Linux: If you want to access the VM instances directly, create a new
Host-onlynetwork calledvboxnet<x>similar to the external OAMone above. Ensure DHCP Server is unchecked, and that the IP address ison a network unrelated to the rest of the addresses we’re configuring.(The default will often be fine.) Now attach adapter-3 to the newHost-only network.
Adapter 4: Internal Network, Name: intnet-data2; Advanced: ParavirtualizedNetwork (virtio-net), Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Additional adapters can be added via command line, for LAG purposes. For example:
Storage nodes:
Adapter 1: Internal Network, Name: intnet-unused; Advanced: IntelPRO/1000MT Desktop, Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Adapter 2: Internal Network, Name: intnet-management; Advanced:Intel PRO/1000MT Desktop, Promiscuous Mode: Allow All
Set the boot priority for interface 2 (eth1) on ALL VMs (controller, workerand storage):
Alternative method for debugging:
Turn on VM and press F12 for the boot menu.
Press
Lfor LAN boot.Press CTL+B for the iPXE CLI (this has a short timeout).
The autoboot command opens a link with each interface sequentiallyand tests for netboot.
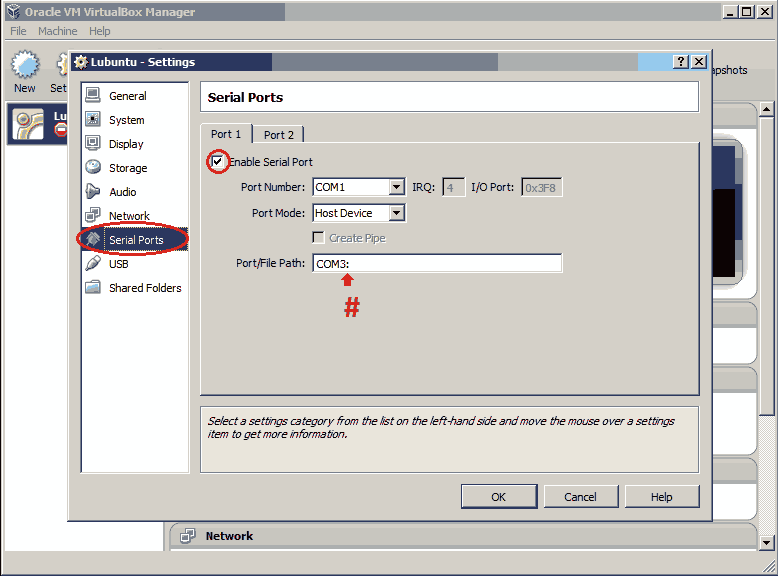
Serial port settings¶

To use serial ports, you must select Serial Console during initial boot usingone of the following methods:
Windows: Select
EnableSerialPort, port mode toHostPipe. SelectCreatePipe(or deselectConnecttoexistingpipe/socket). Entera Port/File Path in the form.pipecontroller-0or.pipeworker-1. Later, you can use this in PuTTY to connect to theconsole. Choose speed of 9600 or 38400.Linux: Select
EnableSerialPortand set the port mode toHostPipe.SelectCreatePipe(or deselectConnecttoexistingpipe/socket).Enter a Port/File Path in the form/tmp/controller_serial. Later, you canuse this withsocatas shown in this example:
Other notes¶
If you’re using a Dell PowerEdge R720 system, it’s important to execute thecommand below to avoid any kernel panic issues:
Console usage:
To use a serial console: Select
SerialControllerNodeInstall, thenfollow the instructions above in theSerialPortsection to connect toit.To use a graphical console: Select
GraphicsTextControllerNodeInstalland continue using the Virtual Box console.

For details on how to specify installation parameters such as rootfs deviceand console port, see Configurable installation parameters.
Follow the StarlingX Installation and Deployment Guidesto continue.
Ensure that boot priority on all VMs is changed using the commands in the “Setthe boot priority” step above.
In an AIO-DX and standard configuration, additionalhosts must be booted using controller-0 (rather than
bootimage.isofile).On Virtual Box, click F12 immediately when the VM starts to select a differentboot option. Select the
lanoption to force a network boot.
StarlingX allows you to specify certain configuration parameters duringinstallation:
Boot device: This is the device that is to be used for the boot partition. Inmost cases, this must be
sda, which is the default, unless the BIOSsupports using a different disk for the boot partition. This is specified withtheboot_deviceoption.Rootfs device: This is the device that is to be used for the rootfs andvarious platform partitions. The default is
sda. This is specified withtherootfs_deviceoption.Install output: Text mode vs graphical. The default is
text. This isspecified with theinstall_outputoption.Console: This is the console specification, allowing the user to specify theconsole port and/or baud. The default value is
ttyS0,115200. This isspecified with theconsoleoption.
Install controller-0 from ISO/USB¶
The initial boot menu for controller-0 is built-in, so modification of theinstallation parameters requires direct modification of the boot command line.This is done by scrolling to the boot option you want (for example, SerialController Node Install vs Graphics Controller Node Install), and hitting thetab key to allow command line modification. The example below shows how tomodify the rootfs_device specification.
Install nodes from active controller¶
The installation parameters are part of the system inventory host details foreach node, and can be specified when the host is added or updated. Theseparameters can be set as part of a host-add or host-bulk-add, host-update, orvia the GUI when editing a host.
For example, if you prefer to see the graphical installation, you can enter thefollowing command when setting the personality of a newly discovered host:
If you don’t set up a serial console, but prefer the text installation, youcan clear out the default console setting with the command:
If you’d prefer to install to the second disk on your node, use the command:
Alternatively, these values can be set from the GUI via the EditHostoption.
I’m been trying to get kernel debugging working with VirtualBox. Both my host and the VM guest are running Windows 7.
Here’s how I was finally able to get it working.
On the VM guest
Created new boot entry with:
- bcdedit /copy {current} /d “Windows with with serial debugging”, copy the created {guid}
- bcdedit /set {guid} debug on
- bcdedit /set {guid} debugport 4, for some reason none of the others ports worked for me
- bcdedit /set {guid} baudrate 115200